What is Edge AI | Definition, Benefits & Applications
Deploying Edge AI: An Overview of Industry Trends and Hardware Selection

Edge AI drives industry transformation by enabling innovations such as smart factories and autonomous systems. But what exactly is it? In this article, we’ll provide a brief overview of Edge AI and explore some of the benefits it offers.
What is Edge AI?
Edge artificial intelligence (AI), aka AI at the edge, involves the deployment of AI algorithms and AI models directly on local edge devices such as sensors or Internet of Things (IoT) devices, enabling real-time data processing and analysis without constant dependence on cloud infrastructure. Combining edge computing devices and AI, Edge AI solutions carry out machine learning tasks directly on connected edge devices. These solutions leverage computing with data stored near where it’s generated, while AI algorithms handle processing right on the device or network edge, without requiring an internet connection. This setup enables data to be processed within milliseconds, delivering real-time results with virtually no latency.
Key benefits of Edge AI
Unlike traditional cloud-based AI, which can be hampered by latency, bandwidth limitations, and privacy concerns, Edge AI brings advanced AI directly to local devices such as sensors, cameras, wearables, and industrial equipment. This shift unlocks several key benefits:
Enhanced AI Capabilities & Real-Time Data Processing
Edge AI allows devices to run advanced algorithms locally, supporting applications like real-time defect detection in manufacturing and instant decision-making in autonomous vehicles. Further, by analyzing data at the source rather than sending it to the cloud for processing, Edge AI delivers responses with ultralow latency. This is vital benefit for mission-critical systems like industrial robots or autonomous cars where even milliseconds matter.
Offline Operation
Because devices equipped with Edge AI can function independently of network connectivity, reliability in environments with unstable or no internet access is ensured. Examples include remote monitoring stations or healthcare facilities.
Lower Operational Costs
Local processing reduces bandwidth usage and energy consumption by minimizing the amount of data transmitted over networks—a key benefit for battery-powered or remote devices.
Stronger Data Privacy & Security
With Edge AI solutions, sensitive information remains on-device instead of being sent across networks. This approach reduces exposure to cyber threats and helps organizations comply with regulations like GDPR and HIPAA.
Scalability & Continuous Improvement
As edge devices proliferate across deployments—from factories to smart cities—they continuously collect valuable operational data. Over time, this enables ongoing refinement of machine learning models at scale without overwhelming central infrastructure or incurring excessive costs.
By integrating these capabilities into sectors such as manufacturing, transportation, healthcare, and retail, Edge AI is driving next-generation efficiency and innovation while addressing challenges related to latency, privacy, cost control, and offline functionality that often limit traditional cloud-based approaches.
Application Scenarios of Edge AI
Edge AI in the Factory
Edge AI is revolutionizing modern manufacturing by improving efficiency, safety, and real-time decision-making on the factory floor. By enabling real-time monitoring of machinery and production lines, Edge AI identifies potential equipment failures before they occur. This supports predictive maintenance, minimizing unplanned downtime and significantly reducing maintenance costs.
With on-site data processing from sensors and cameras, Edge AI detects product defects and anomalies instantly—ensuring higher quality control without relying on cloud-based systems. It also empowers factories to automate complex workflows by enabling low-latency, high-speed decision-making at the edge, resulting in improved productivity and operational efficiency. Additionally, real-time monitoring of workers enhances workplace safety, allowing for immediate alerts and interventions, if necessary, to help prevent accidents.

Edge AI in Smart Cities
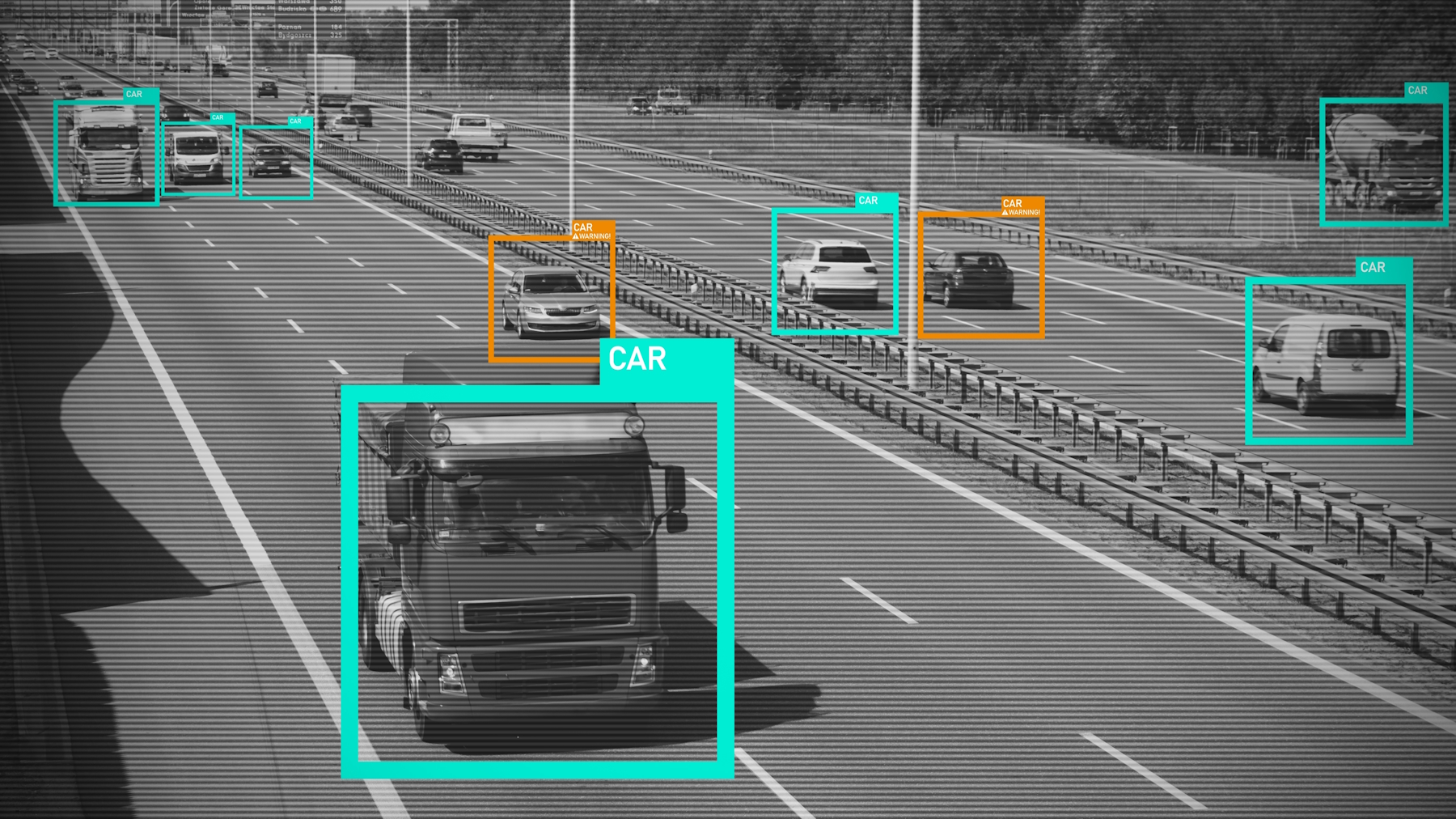
When it comes to smart cities, Edge AI can process data from traffic cameras and sensors to optimize traffic flow, reduce congestion, and improve public transportation efficiency. It can also provide real-time updates to commuters.
By analyzing live video feeds and sensor data locally, Edge AI enables rapid detection and response to emergencies, crimes, and accidents, improving public safety and emergency response times. In smart buildings and infrastructure, Edge AI optimizes energy consumption by dynamically adjusting HVAC systems and street lighting based on real-time usage patterns, driving down energy costs and helping reduce carbon footprint.
Edge AI also supports environmental monitoring, analyzing data from air quality and noise sensors to enable timely interventions and promote healthier urban living conditions.
Choosing an Edge AI Solution
Edge AI is rapidly transforming industries by enabling organizations to streamline operations, automate tasks, and drive innovation—ultimately improving efficiency and delivering strong ROI. When selecting an Edge AI platform, engineers face a complex landscape of options and must make critical decisions regarding several key factors, as listed below.
Processing Power
The platform’s CPU must be capable of handling the required AI workloads. Compatibility with leading CPUs and GPUs—such as those from Intel®—is essential for ensuring high performance in real-time inferencing scenarios. It is also crucial to confirm that the platform supports necessary AI frameworks and libraries for smooth development and deployment.
Ruggedness
For industrial or outdoor environments, choose a platform engineered to withstand harsh conditions like extreme temperatures, dust, moisture, and vibrations. Look for certifications such as IP ratings that validate the system’s robustness.
Security
Ensure your chosen platform offers advanced security features including encryption, secure boot processes, and trusted platform modules (TPM). Also, confirm support for secure software development practices and availability of regular updates to address vulnerabilities.
Integration
The Edge AI system should integrate seamlessly with existing sensors, cameras, hardware components—and be compatible with your current software stack. Easy integration with cloud services, IoT platforms, and enterprise systems is vital to ensure interoperability across protocols in place.
Supply Chain Stability
Partnering with reputable suppliers who have a proven track record of consistent delivery is critical. Evaluate their history through customer reviews; ensure long-term availability of both components and platforms to avoid obsolescence or disruptions; consider technical support quality as well as warranty terms.
Consider ASUS Edge AI Solutions
ASUS IoT is a standout provider in the Edge AI space, delivering solutions that harness the latest Intel CPU/GPU technology combined with advanced AIoT capabilities. ASUS IoT platforms are designed for scalability and performance, and they are also flexible enough to excel in diverse applications—from real-time edge inferencing to demanding industrial automation tasks.
One focus that sets ASUS IoT apart is a commitment to durability. ASUS offers many Edge AI systems featuring ruggedized builds—fanless designs resistant to vibration—with wide temperature tolerance ranges and low power consumption profiles. These attributes make them ideal for factory automation environments where reliability under stress is vital.

By integrating robust engineering with cutting-edge computing power—and backing it all up with strong supply chain reliability—ASUS IoT empowers organizations at the forefront of Edge AI innovation, driving efficiency even in the most challenging operational scenarios. For those seeking next-generation edge solutions built on proven Intel architectures coupled with industry-leading ruggedness and strong after-sales support, ASUS IoT stands ready to deliver transformative results.
Click here to learn more about ASUS IoT Edge AI Systems and ASUS IoT.
